in the visible light spectrum
for the very first time.
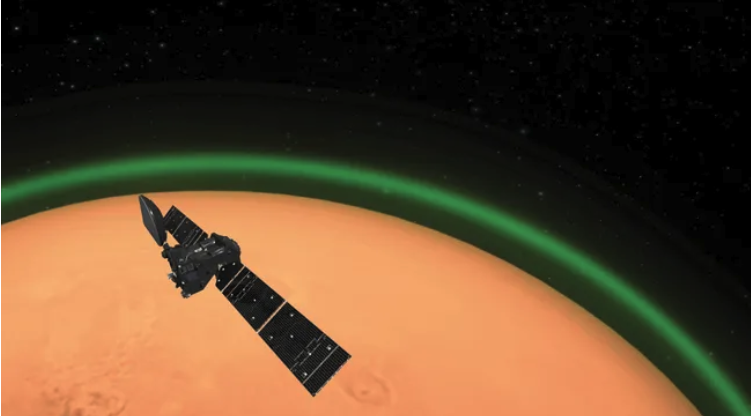
Mars might be the Red Planet, but its atmosphere glows green.
Using the European Space Agency's (ESA) ExoMars
Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO), scientists have observed
Mars' atmosphere glowing green for the first time ever
— in the visible light spectrum, that is.
The effect is called airglow
(or dayglow or nightglow, depending on the hour),
and it occurs on Earth, too.
While it shares some similarities with the northern lights
(or aurora) here on our planet,
it's a different phenomenon with different causes.
Nightglow, in particular, "occurs when two oxygen atoms combine to form an oxygen molecule,"
according to ESA, ExoMars. On Mars, this happens at an altitude of approximately 31 miles (50 km).
By comparison, auroras occur when charged particles from the sun collide with Earth's magnetic field.
Scientists have suspected Mars to have airglow
for some 40 years, but the first observation only occurred a decade ago by ESA's Mars Express orbiter, which detected the phenomenon in the infrared spectrum.
Then, in 2020, scientists observed the phenomenon in visible light using TGO, but in Martian daylight rather than at night. Now, we've seen the phenomenon at night
via TGO (Trace Gas Orbiter). -Stefanie Waldek
























 RSS Feed
RSS Feed